If you sell to US clients from Pakistan or anywhere outside the US, you will face this question:
Do you need to charge sales tax on your invoice?
Many foreign founders guess.
That guess becomes expensive.
US sales tax is state-level, not federal. Each state sets its own rules, rates, and thresholds.
After South Dakota v. Wayfair (2018), states can require remote sellers to collect sales tax based on economic nexus (sales activity in a state), even with no physical presence.
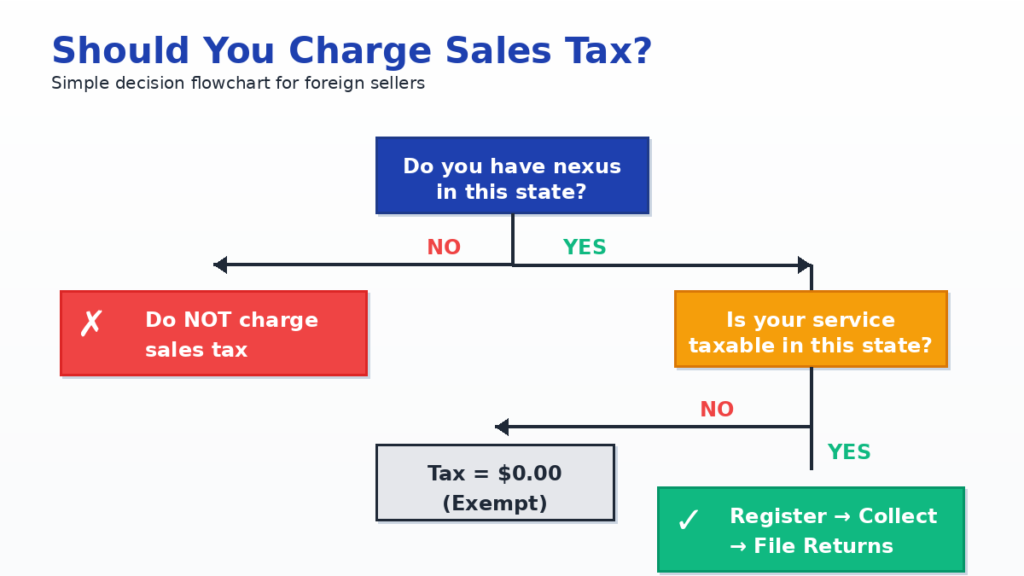
This guide gives you one clear rule:
- If you have nexus in a state, register and collect tax at sale.
- If you have no nexus, do not charge sales tax.
Example: Texas expects collection once you cross its remote seller threshold ($500,000 in Texas revenue over the prior 12 months).
Next, we will break down nexus in simple terms, then move straight into invoicing and collection steps you can copy.
Why Does This Matter More Than You Think?
Sales tax becomes a problem when founders treat it as optional.
Before 2018, most states focused on physical presence.
No office or staff often meant no collection.
That changed after South Dakota v. Wayfair (2018).
States can now enforce sales tax based on economic nexus alone.
This matters because:
- You can sell from Pakistan and still trigger state tax rules.
- Crossing a state threshold creates a legal duty to register and collect.
- If you skip collection and the state reviews your activity later, the bill lands on you, not your client.
One clear example:
- You sell SaaS into Texas.
- Texas uses a remote seller threshold of $500,000 in Texas revenue over the prior 12 months.
- Cross it, and Texas expects registration and collection going forward.
Location does not protect you.
Only your nexus status does.
Common Myths That Cost Foreign Founders Money
Sales tax mistakes usually start with bad assumptions.
Here are the ones that cause the most damage.
Myth 1: “I’m not a US company, so sales tax doesn’t apply”
False.
Sales tax depends on where your customer is, not where you live.
If you have nexus in a state, that state can require you to collect tax.
Your passport, bank account, or country of incorporation does not change that.
Myth 2: “US clients will be upset if I add sales tax”
This fear is exaggerated.
US businesses see sales tax on invoices every day.
For B2B clients, sales tax is a pass-through charge, not a price increase.
If a state requires collection and you skip it, the risk falls on you, not the client.
That usually costs more than charging tax correctly from day one.
A clean explanation is enough:
“Sales tax is required by state law once thresholds are crossed. It appears as a separate line on the invoice.”
Myth 3: “Only physical products are taxable”
Wrong.
Many states tax digital products and SaaS.
Some states even tax certain services.
Examples:
- SaaS is taxable in states like Texas and New York.
- SaaS is not taxable in California.
- Consulting services are often exempt, but not everywhere.
This is why you must check taxability by state, not assume.
Myth 4: “I’ll deal with sales tax later when I’m bigger”
This mindset creates backdated problems.
States do not wait for you to feel ready.
They care about when you crossed the threshold, not when you noticed it.
Once nexus exists, delays increase cleanup cost.
Understanding Economic Nexus (When Collection Starts)
Economic nexus answers one question:
Have you sold enough into a state that the state can force you to collect sales tax?
You do not need:
- an office
- an employee
- a US address
Sales volume alone can trigger it.
How economic nexus works
Each state sets a threshold.
Cross it, and the obligation starts.
States measure thresholds using:
- revenue, or
- transaction count, or
- both
The time window also varies:
- prior 12 months
- prior four quarters
- current or prior calendar year
This is why founders get confused.
Common economic nexus thresholds (quick view)
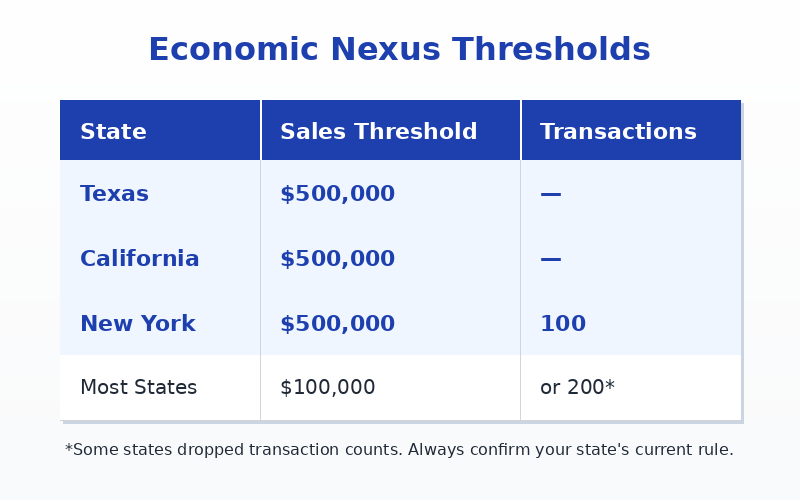
Important:
- Thresholds usually count total sales, not only taxable sales.
- Taxability decides what is taxed, not whether nexus exists.
Simple example
You run a SaaS business.
Last 12 months:
- Texas: $150,000
- California: $80,000
- New York: $60,000
Result:
- No economic nexus yet.
- You do not charge sales tax.
Later:
- Texas sales reach $520,000 within 12 months.
Result:
- Economic nexus exists in Texas.
- You must register in Texas.
- You must collect sales tax on future Texas invoices.
Nothing else changed.
Only the threshold did.
What economic nexus does not mean?
- It does not mean you owe tax in every state.
- It does not mean you charge tax retroactively by default.
- It does not mean every service becomes taxable.
It only means:
“This state can now require you to collect.”
Is Your Service Actually Taxable?
Economic nexus tells you where you may need to collect.
Taxability tells you what you collect tax on.
Both matter.
Nexus alone does not mean every invoice gets tax.
Start with this rule
After nexus exists, you ask one question per state:
Does this state tax what I sell?
The answer depends on the service type.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS tax rules vary by state.
Common patterns you must know:
- Taxable
- Texas (treated as a data processing service)
- New York
- Washington
- Texas (treated as a data processing service)
- Not taxable
- California
- Several other states
- California
Texas is a frequent trap for SaaS founders.
Texas treats SaaS under “data processing services,” which makes it taxable once nexus exists
Guidance comes from the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts.
Texas also allows a partial exemption:
- Only 80% of the SaaS charge is taxable.
- 20% is exempt.
This affects invoice math, not nexus.
Consulting And Professional Services
Most states do not tax pure consulting.
Examples:
- Strategy
- Marketing advice
- Business consulting
Exceptions exist.
Some states tax broad service categories, including:
- Hawaii
- New Mexico
- South Dakota
Texas does not tax consulting services.
A Pakistani consultant billing Texas clients usually charges no sales tax, even if nexus exists.
Digital Products
Digital goods include:
- Online courses
- Ebooks
- Downloadable files
Taxability varies widely by state.
Some states tax them.
Others do not.
Never assume digital means exempt.
What founders often get wrong
- Thinking SaaS is exempt everywhere
- Thinking consulting is taxable everywhere
- Mixing VAT logic with US sales tax logic
US sales tax is state-by-state, not category-wide.
Practical takeaway
Once nexus exists:
- You do not automatically tax every invoice.
- You tax only what the state defines as taxable.
What To Do Once Nexus And Taxability Are Confirmed
At this point, two things are true:
- You have a nexus in a state.
- Your service is taxable in that state.
Now action matters. Delay creates risk.
Step 1: Register Before You Charge
You cannot legally collect sales tax without registration.
Each state issues its own sales tax permit.
Example: Texas registration happens through the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts.
Key rules:
- Do not add tax to invoices before approval.
- Registration often takes days to a few weeks.
- Many states charge no fee, but some do.
Charging tax without a permit looks worse than not charging at all.
Step 2: Decide How You Will Collect Tax
You have two clean options.
Option A: Add Sales Tax On Top Of Your Price
This is the safest and most common approach.
How it works:
- You quote your service price.
- Sales tax appears as a separate line.
- The customer pays both.
This works well for:
- Freelancers
- Consultants
- Custom SaaS plans
Option B: Include Tax Inside Your Price
Some SaaS founders prefer flat pricing.
How it works:
- You quote one number.
- You back out the tax internally.
- Your margin absorbs the tax.
This keeps pricing simple but requires clean records.
Never mix both approaches without tracking.
Invoice Templates: How To Charge Sales Tax Correctly
Invoices are where founders mess up most.
This section removes guesswork.
Each template below solves a real scenario foreign sellers face.
Template 1: SaaS Invoice (Texas Client, Sales Tax Added)
Use this when:
- You crossed Texas’s nexus threshold
- Your SaaS is taxable in Texas
- You charge tax on top of your price
Invoice Example
Service: Monthly SaaS Subscription
Price: $100.00
Sales Tax (TX 8.25%): $8.25
Total Due: $108.25
Why this works
- Sales tax is shown as a separate line
- Rate is correct (Texas max is 8.25%)
- Client sees tax as a legal pass-through
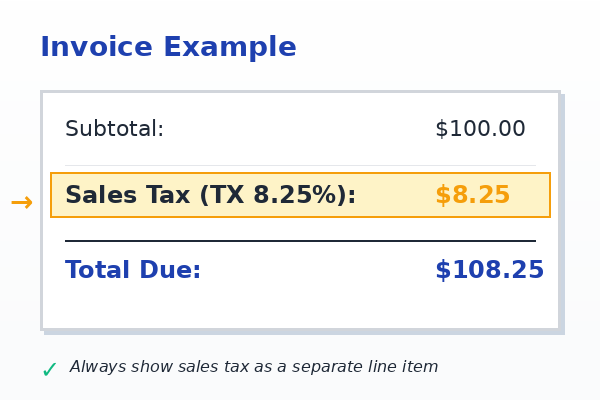
This is the safest structure for audits.
Template 2: SaaS Invoice (Texas, 80% Taxable Rule Applied)
Use this when:
- You sell SaaS in Texas
- You apply the data processing rule
- Only 80% of the charge is taxable
Invoice Example
Service: Monthly SaaS Subscription
Price: $100.00
Taxable Portion (80%): $80.00
Sales Tax (TX 8.25%): $6.60
Total Due: $106.60
Why this works
- Correct taxable base
- Correct math
- Matches Texas data processing treatment
This protects you if Texas reviews your invoices.
Template 3: Consulting Invoice (Texas Client, No Sales Tax)
Use this when:
- You provide consulting
- Consulting is exempt in that state
- Nexus exists, but taxability does not
Invoice Example
Service: Business Consulting (March 2026)
Price: $2,000.00
Sales Tax: $0.00 (Service exempt under state law)
Total Due: $2,000.00
Why this works
- Shows you reviewed taxability
- Avoids overcharging
- Documents exemption clearly
Never leave tax blank.
Explicitly show $0.00.
Template 4: No-Nexus Invoice (Any State)
Use this when:
- You have not crossed a threshold
- You are not required to collect
Invoice Example
Service: SaaS Subscription
Price: $100.00
Sales Tax: Not charged (no nexus)
Total Due: $100.00
Why this works
- Clear explanation
- Reduces client questions
- Creates an audit trail
What Every Invoice Must Include?
Regardless of template, include:
- Your business name
- Customer name and address
- Subtotal before tax
- Sales tax line (even if $0.00)
- Total due
- Your sales tax permit number (when registered)
Missing these details creates risk.
Should You Add Tax On Top Or Include It In Your Price?
Both are allowed.
Add tax on top
- Clean
- Transparent
- Best for freelancers and consultants
Include tax in price
- Simple pricing
- Requires internal tax math
- Margin absorbs tax
Pick one.
Track it properly.
Do not mix without records.
How To Calculate Rates Without Guessing
Guessing rates causes under-collection or over-collection.
Both are problems.
Manual Method (Small Volume)
You can:
- Use a state rate lookup tool
- Enter the customer ZIP code
- Apply the correct rate
This works only at low volume.
Automated Method (Recommended)
Tools handle:
- Rate calculation
- Threshold tracking
- Reporting
Popular options:
- Stripe Tax
- TaxJar
These tools reduce human error.
Payoneer Workflow (Simple Way To Stay Clean)
Payoneer does not file your sales tax for you.
Payoneer helps you get paid and keep billing organized.
Use Payoneer as the payment rail.
Use your invoice system to handle tax lines.
Here is a clean workflow you can follow:
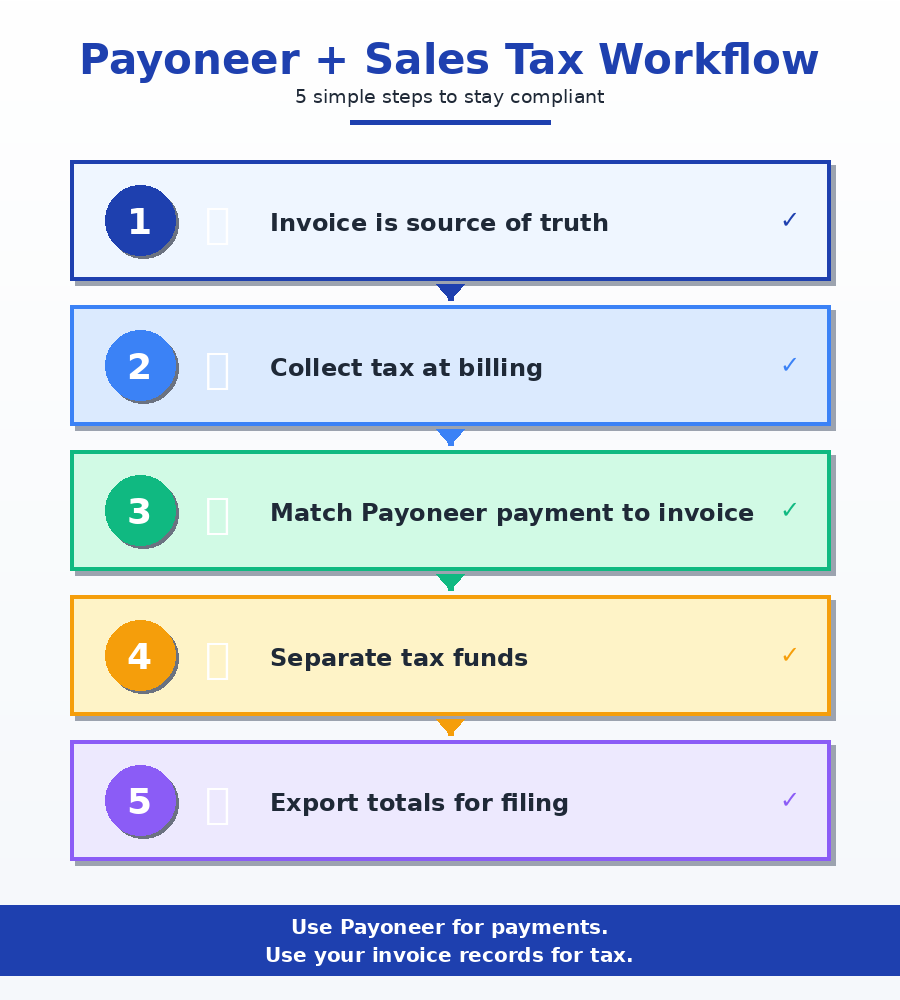
Step 1: Keep your invoice as the source of truth
- Generate invoices from one system.
- Do not “make invoices” inside emails or WhatsApp.
- Your invoice must show:
- Subtotal
- Sales tax line
- Total due
- Permit number (when registered)
- Subtotal
Step 2: Collect tax at the time you bill
- If nexus exists, charge sales tax on the invoice.
- Do not collect tax “later” after payment.
- States expect tax charged at sale, not patched afterward.
Step 3: Match Payoneer payments to invoices
- Save the Payoneer transaction ID with each invoice record.
- Keep a simple log:
- Invoice number
- Client state
- Subtotal
- Tax collected
- Total paid
- Payment date
- Invoice number
This log saves you during filing.
Step 4: Separate tax money from business money
- Transfer the tax portion into a separate bucket or account.
- Do not spend collected tax.
- The collected tax is state money.
Step 5: Export monthly totals for filing
At the end of the month, export totals by state:
- Total sales
- Taxable sales
- Sales tax collected
Then file through:
- the state portal, or
- a tool like Stripe Tax / TaxJar
This keeps Payoneer in its lane and keeps you compliant.
When You Should NOT Charge Sales Tax?
Overcharging creates refunds and trust issues.
Do not charge sales tax when:
You Have No Nexus
If you did not cross thresholds:
- Do not collect tax.
- Do not register early “just in case.”
The Client Is In A No-Sales-Tax State
These states have no state sales tax:
- Delaware
- Oregon
- Montana
- New Hampshire
- Alaska
(Some local taxes still exist in Alaska.)
Your Service Is Exempt In That State
Common examples:
- Consulting in Texas
- Consulting in California
Exemption does not remove filing duties if nexus exists.
Filing And Remitting Tax (The Quiet Obligation)
Once registered, filing never stops.
Even if:
- You had no sales
- You collected zero tax
Some states require filings even with $0 tax. Confirm your state’s rules.
Texas example:
- Monthly or quarterly filing
- Deadlines vary by state. Texas often uses the 20th.
Collected tax is not your money.
Keep it separate.
Final Thoughts
Sales tax is not something foreign founders can ignore anymore.
If you sell to US clients and cross a state’s threshold, the obligation starts.
Not when you feel ready.
Not when a client complains.
At the moment nexus exists.
The good news is this:
Sales tax becomes manageable once you treat it as a process, not a mystery.
- Track sales by state
- Watch thresholds
- Register on time
- Charge tax clearly on invoices
- File and remit what you collect
Do this, and sales tax stops being a risk.
Skip it, and the cleanup always costs more.
Need Help Getting This Right?
If you are unsure about:
- whether you have nexus
- whether your service is taxable
- how to fix past invoices
- how to set up clean, compliant invoicing
Do not guess.
Contact us and get clarity before it turns into a liability.
A short review today can save you penalties, back taxes, and painful cleanups later.
Disclaimer: This article is authored by a writer at Scounts Private Limited. Please note that the fees mentioned are subject to change and may not be accurate at the time of reading. The content has not yet reviewed by any of our LLC taxation experts. For expert advice or services, feel free to contact us.
